As Unit 4 Worksheet 3 Chemistry takes center stage, let’s delve into the fascinating world of chemical bonding, reactions, acids and bases, electrochemistry, and organic chemistry. Get ready for an engaging exploration of the fundamental principles that govern the interactions of matter.
Chemical bonding, the glue that holds atoms together, forms the foundation of our understanding of chemistry. We’ll explore the diverse types of bonds, their properties, and the molecules they create.
Chemical Bonding: Unit 4 Worksheet 3 Chemistry
Chemical bonding is the process by which atoms are held together to form molecules and compounds. There are three main types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, and metallic.
Unit 4 worksheet 3 chemistry has a lot of challenging questions, but it’s worth it to learn about the fascinating history of dust bowl migrant for short . It’s incredible how much we’ve learned about chemistry since then, and this worksheet is a great way to review the basics.
Ionic Bonds
Ionic bonds are formed between a metal and a nonmetal. In an ionic bond, one atom gives up one or more electrons to another atom. The atom that gives up electrons becomes a positively charged ion, and the atom that receives electrons becomes a negatively charged ion.
The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by the electrostatic force, forming an ionic bond.
Ionic bonds are typically strong and have high melting and boiling points. Ionic compounds are usually soluble in water.
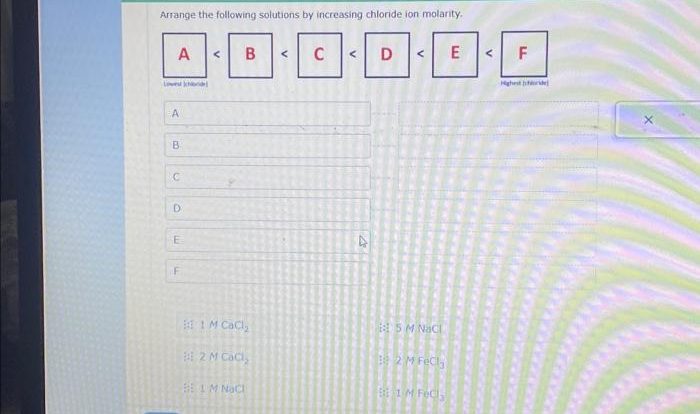
Examples of ionic bonds include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl), and calcium fluoride (CaF2).
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds are formed between two nonmetal atoms. In a covalent bond, the atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, forming a covalent bond.
Covalent bonds are typically weaker than ionic bonds and have lower melting and boiling points. Covalent compounds are usually insoluble in water.
Examples of covalent bonds include hydrogen (H2), oxygen (O2), and water (H2O).
Metallic Bonds
Metallic bonds are formed between metal atoms. In a metallic bond, the metal atoms share their valence electrons in a sea of electrons. The valence electrons are not attached to any particular atom, but they are free to move around the metal.
Metallic bonds are typically strong and have high melting and boiling points. Metallic compounds are usually good conductors of heat and electricity.
Examples of metallic bonds include sodium (Na), potassium (K), and aluminum (Al).
Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions are processes that involve the transformation of one set of chemical substances into another. They are essential for life and occur all around us, from the burning of fuels to the digestion of food.
Types of Chemical Reactions
There are many different types of chemical reactions, but they can be broadly classified into five main categories:
- Combination reactionsoccur when two or more substances combine to form a single product.
- Decomposition reactionsoccur when a single substance breaks down into two or more products.
- Single-replacement reactionsoccur when one element replaces another element in a compound.
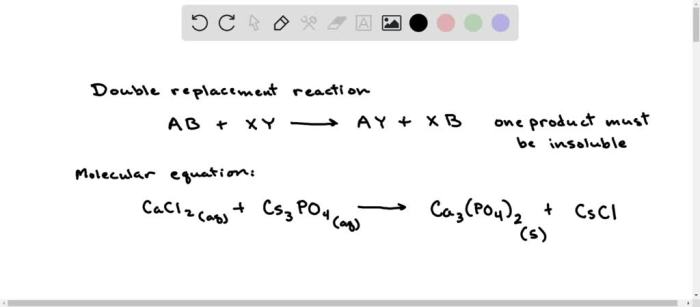
- Double-replacement reactionsoccur when two compounds exchange ions to form two new compounds.
- Combustion reactionsoccur when a substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light.
Factors that Affect the Rate of a Chemical Reaction
The rate of a chemical reaction is determined by a number of factors, including:
- Concentration of the reactants: The higher the concentration of the reactants, the faster the reaction will occur.
- Temperature: The higher the temperature, the faster the reaction will occur.
- Surface area of the reactants: The greater the surface area of the reactants, the faster the reaction will occur.
- Presence of a catalyst: A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed in the reaction.
Acids and Bases
Acids and bases are two fundamental concepts in chemistry that describe the chemical properties of substances. Acids are substances that donate protons (H+ ions), while bases are substances that accept protons.The properties of acids and bases are often described in terms of their pH.
The pH scale is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, while a pH below 7 is acidic and a pH above 7 is basic.
Acids
Acids have several characteristic properties:
- They taste sour.
- They turn blue litmus paper red.
- They react with metals to produce hydrogen gas.
- They react with bases to produce salt and water.
Bases, Unit 4 worksheet 3 chemistry
Bases also have several characteristic properties:
- They taste bitter.
- They turn red litmus paper blue.
- They feel slippery to the touch.
- They react with acids to produce salt and water.
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical change. It is a fundamental part of many technologies, including batteries, fuel cells, and corrosion control.Electrochemical cells are devices that use chemical reactions to generate electricity or to drive chemical reactions.
There are two main types of electrochemical cells: galvanic cells and electrolytic cells. Galvanic cells generate electricity from a spontaneous chemical reaction, while electrolytic cells use electricity to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction.Electrochemistry has a wide range of applications, including:* Batteries: Batteries are electrochemical cells that store chemical energy and convert it to electrical energy when needed.
Fuel cells
Fuel cells are electrochemical cells that convert the chemical energy of a fuel, such as hydrogen or natural gas, into electrical energy.
Corrosion control
Electrochemistry is used to study and control corrosion, which is the deterioration of metals due to chemical reactions with their environment.
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon. Carbon is a unique element that can form long chains and rings, which gives rise to the vast diversity of organic molecules.
Types of Organic Molecules
Organic molecules can be classified into several types based on their functional groups. Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms that give organic molecules their characteristic properties.
- Alkanes: Contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms and have a single bond between each carbon atom.
- Alkenes: Contain carbon-carbon double bonds.
- Alkynes: Contain carbon-carbon triple bonds.
- Alcohols: Contain a hydroxyl group (-OH).
- Ethers: Contain an ether group (-O-).
- Aldehydes: Contain a carbonyl group (-C=O) and a hydrogen atom.
- Ketones: Contain a carbonyl group (-C=O) and two alkyl groups.
- Carboxylic acids: Contain a carboxyl group (-COOH).
- Esters: Contain an ester group (-COOR).
- Amides: Contain an amide group (-CONH2).
Properties of Organic Molecules
Organic molecules have several characteristic properties:
- Covalent bonding: Organic molecules are held together by covalent bonds, which are formed when atoms share electrons.
- Low melting and boiling points: Organic molecules have low melting and boiling points because they have weak intermolecular forces.
- Solubility: Organic molecules are generally insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents.
- Combustibility: Organic molecules are combustible and burn in the presence of oxygen.
- Reactivity: Organic molecules can undergo a wide variety of chemical reactions.
FAQ
What is the significance of chemical bonding?
Chemical bonding determines the structure and properties of all matter, from the smallest molecules to the largest macromolecules.
How do chemical reactions affect our daily lives?
Chemical reactions are responsible for everything from cooking food to powering our cars and generating electricity.
What is the importance of acids and bases in chemistry?
Acids and bases are crucial for maintaining the pH balance in living organisms and play vital roles in industrial processes.
How does electrochemistry impact modern technology?
Electrochemistry is the foundation for batteries, fuel cells, and other electrochemical devices that power our electronic gadgets.
What is the scope of organic chemistry?
Organic chemistry encompasses the study of carbon-containing compounds, which are the building blocks of life and essential for countless industrial applications.