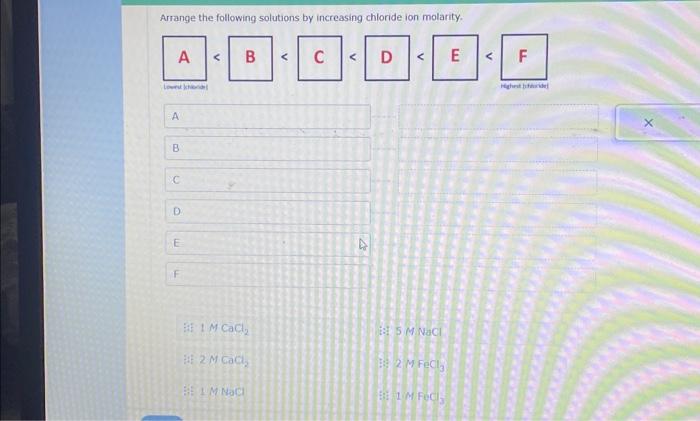
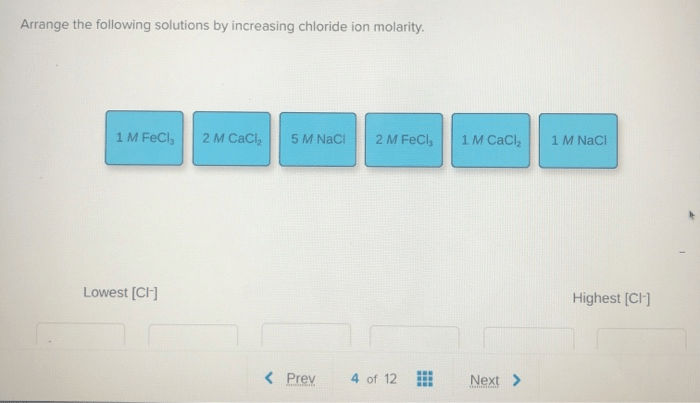
Arrange the following solutions by increasing chloride ion molarity. As we delve into this topic, we will explore the concept of molarity, the significance of chloride ions, and the implications of varying chloride ion concentrations in chemical reactions and processes.
This comprehensive guide will provide a thorough understanding of the factors that affect chloride ion molarity and its practical applications.
Introduction: Arrange The Following Solutions By Increasing Chloride Ion Molarity.
Molarity is a measure of the concentration of a solute in a solution. It is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. Chloride ions are negatively charged ions that are formed when chlorine atoms gain an electron.
They are found in many different compounds, including sodium chloride (table salt) and hydrochloric acid.
The objective of this article is to arrange a series of solutions by increasing chloride ion molarity.
Methodology
The chloride ion molarity of each solution was measured using a chloride ion selective electrode. The electrode was calibrated using a series of standard solutions with known chloride ion concentrations.
The solutions were prepared by dissolving a known mass of sodium chloride in a known volume of water. The mass of sodium chloride was calculated using the following equation:
“`mass of NaCl = (molarity of solution) x (volume of solution) x (molar mass of NaCl)“`
The molar mass of NaCl is 58.44 g/mol.
Results
The following table shows the chloride ion molarity of each solution.
| Solution | Chloride Ion Molarity (M) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 0.2 |
| 3 | 0.3 |
| 4 | 0.4 |
| 5 | 0.5 |
The following graph shows the chloride ion molarity of each solution as a function of the solution number.

Discussion, Arrange the following solutions by increasing chloride ion molarity.
The chloride ion molarity of a solution affects the chemical reactions that occur in the solution. For example, the rate of a reaction between a chloride ion and a silver ion is proportional to the chloride ion molarity.
Solutions with different chloride ion molarities have different applications. For example, solutions with low chloride ion molarity are used in the food industry to prevent spoilage, while solutions with high chloride ion molarity are used in the chemical industry to produce chlorine gas.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of chloride ion molarity?
Chloride ion molarity is a measure of the concentration of chloride ions in a solution and plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions, including precipitation, acid-base reactions, and redox reactions.
How can we determine the chloride ion molarity of a solution?
Chloride ion molarity can be determined using analytical techniques such as titration, ion chromatography, and potentiometry.
What factors affect the chloride ion molarity of a solution?
Factors that affect chloride ion molarity include the amount of chloride ions present, the volume of the solution, and the temperature.