Reactions in aqueous solutions metathesis reactions and net ionic equations – Reactions in aqueous solutions, particularly metathesis reactions and net ionic equations, form the cornerstone of understanding chemical interactions in water-based environments. Metathesis reactions involve the exchange of ions between reactants, while net ionic equations focus on the essential ions involved in the reaction, excluding spectator ions.
This discussion delves into the intricacies of metathesis reactions, exploring their types, predicting their products, and writing net ionic equations. Furthermore, we examine the practical applications of these reactions in various fields, including industry, environmental chemistry, and everyday life.
Reactions in Aqueous Solutions: Reactions In Aqueous Solutions Metathesis Reactions And Net Ionic Equations

Reactions in aqueous solutions are chemical reactions that occur in water. Water is a polar solvent, meaning it has a positive end and a negative end. This polarity allows water to dissolve ionic compounds, which are compounds that contain positively and negatively charged ions.
When ionic compounds dissolve in water, the ions are separated from each other and become surrounded by water molecules.
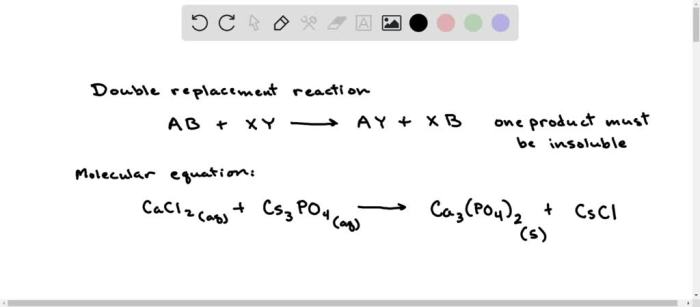
Metathesis reactions are a type of chemical reaction in which two ionic compounds exchange ions to form two new ionic compounds. Metathesis reactions are also known as double displacement reactions. The general equation for a metathesis reaction is:
AB + CD → AD + CB
In this equation, A, B, C, and D represent the ions of the reactants and products. Metathesis reactions can be used to prepare a variety of different compounds, including precipitates, gases, and acids.
Net ionic equations are equations that show only the ions that are actually reacting in a chemical reaction. The spectator ions, which are ions that do not participate in the reaction, are omitted from the net ionic equation. Net ionic equations are useful for understanding the essential features of a chemical reaction.
Types of Metathesis Reactions, Reactions in aqueous solutions metathesis reactions and net ionic equations
There are three main types of metathesis reactions:
- Precipitation reactionsoccur when two ionic compounds react to form a solid precipitate. The precipitate is a compound that is insoluble in water.
- Gas-forming reactionsoccur when two ionic compounds react to form a gas. The gas is usually a product of a reaction between an acid and a base.
- Acid-base reactionsoccur when an acid and a base react to form a salt and water. Salts are ionic compounds that are soluble in water.
The type of metathesis reaction that occurs depends on the reactants involved. For example, if one of the reactants is a strong acid, then the reaction will likely be an acid-base reaction. If one of the reactants is a weak acid, then the reaction will likely be a precipitation reaction.
Predicting Products of Metathesis Reactions
The products of a metathesis reaction can be predicted using the solubility rules. The solubility rules are a set of rules that predict whether a compound is soluble in water. The solubility rules are as follows:
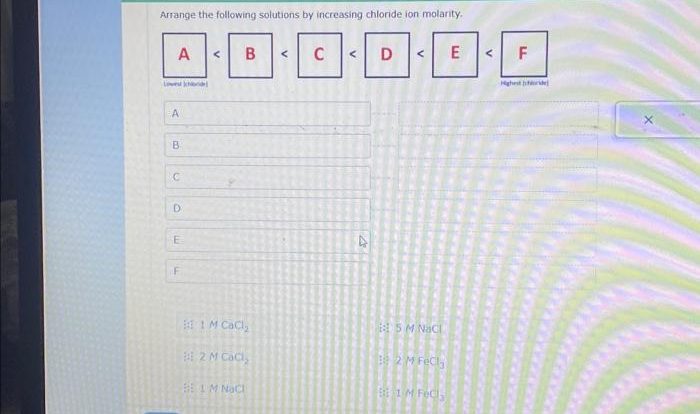
- All Group 1 cations (Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, Cs+) are soluble.
- All Group 2 cations (Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+) are soluble, except for BaSO4.
- All ammonium (NH4+) cations are soluble.
- All nitrate (NO3-) anions are soluble.
- All chloride (Cl-) anions are soluble, except for AgCl, PbCl2, and Hg2Cl2.
- All bromide (Br-) anions are soluble, except for AgBr, PbBr2, and Hg2Br2.
- All iodide (I-) anions are soluble, except for AgI, PbI2, and Hg2I2.
- All sulfate (SO42-) anions are soluble, except for BaSO4 and SrSO4.
- All carbonate (CO32-) anions are insoluble, except for Na2CO3, K2CO3, and CaCO3.
- All phosphate (PO43-) anions are insoluble, except for Na3PO4, K3PO4, and NH43PO4.
- All hydroxide (OH-) anions are insoluble, except for NaOH, KOH, and Ca(OH)2.
To predict the products of a metathesis reaction, first identify the cations and anions of the reactants. Then, use the solubility rules to determine whether the products will be soluble or insoluble. If the products are insoluble, then they will precipitate out of solution.
Writing Net Ionic Equations
Net ionic equations are written by first identifying the spectator ions. Spectator ions are ions that do not participate in the reaction. To identify the spectator ions, look for ions that appear on both sides of the equation. Once the spectator ions have been identified, they can be removed from the equation.
The remaining ions are the ions that are actually reacting, and they are the ions that are included in the net ionic equation.
Here are the steps for writing a net ionic equation:
- Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
- Identify the spectator ions. Spectator ions are ions that appear on both sides of the equation.
- Remove the spectator ions from the equation. The remaining ions are the ions that are actually reacting.
- Write the net ionic equation using the remaining ions.
Applications of Metathesis Reactions
Metathesis reactions have a wide variety of applications in industry, environmental chemistry, and everyday life.
- Industrial applications:Metathesis reactions are used to produce a variety of industrial chemicals, including plastics, pharmaceuticals, and fertilizers.
- Environmental chemistry:Metathesis reactions are used to remove pollutants from water and soil.
- Everyday life:Metathesis reactions are used in a variety of everyday products, including antacids, toothpaste, and deodorants.
Q&A
What are the different types of metathesis reactions?
Metathesis reactions can be classified into three main types: precipitation reactions, acid-base reactions, and redox reactions.
How do you predict the products of a metathesis reaction?
Predicting the products of a metathesis reaction involves using solubility rules to determine whether the ions will form a precipitate. If a precipitate forms, it will be one of the products.
What is the purpose of writing net ionic equations?
Net ionic equations are used to represent the essential ions involved in a reaction, excluding spectator ions. They provide a simplified and more informative representation of the chemical change.