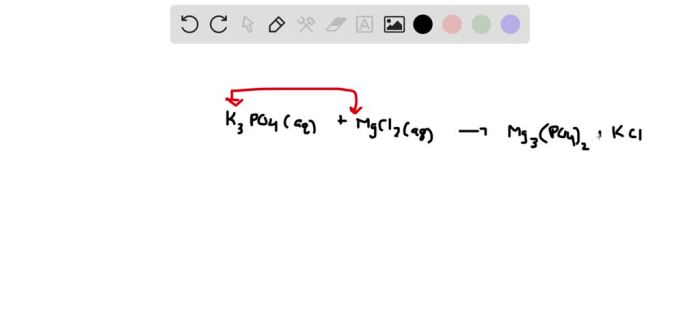
The K3PO4 + MgCl2 precipitation reaction, a captivating chemical phenomenon, unveils the intricate dance of ions and molecules as they transform into a solid precipitate. This reaction, with its unique properties and practical applications, invites us on an enlightening journey into the realm of precipitation chemistry.
The reactants, K3PO4 (potassium phosphate) and MgCl2 (magnesium chloride), embark on a fascinating transformation when combined. As the solutions mingle, their ions engage in an intricate exchange, leading to the formation of a new compound: Mg3(PO4)2, which manifests as a solid precipitate.
Introduction to the Precipitation Reaction
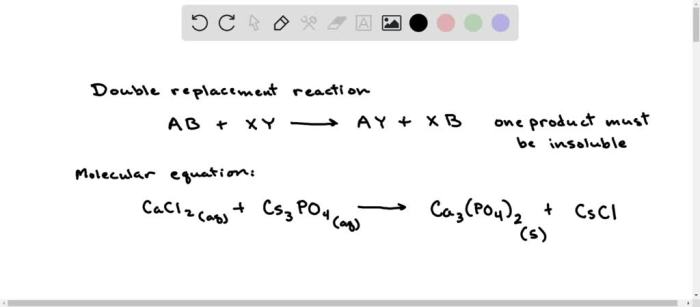
Precipitation reactions occur when two soluble ionic compounds react in a solution to form an insoluble solid compound, known as the precipitate. These reactions are commonly used to separate ions from a solution or to prepare specific chemical compounds.
In the precipitation reaction between K 3PO 4and MgCl 2, the cations (K +and Mg 2+) and anions (PO 43-and Cl –) present in the solution interact to form an insoluble solid compound, magnesium phosphate (Mg 3(PO 4) 2), which precipitates out of the solution.
Chemical Equation
The chemical equation for the precipitation reaction between K 3PO 4and MgCl 2is as follows:
K3PO 4(aq) + 3MgCl 2(aq) → Mg 3(PO 4) 2(s) + 6KCl(aq)
In this reaction, the solid precipitate, Mg 3(PO 4) 2, forms when the ions K +, PO 43-, Mg 2+, and Cl –interact in the solution.
Reactants and Products

In the precipitation reaction between K3PO4 and MgCl2, the reactants and products involved are as follows:
Reactants
- Potassium Phosphate (K3PO4): A white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. It is a source of potassium and phosphate ions.
- Magnesium Chloride (MgCl2): A white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. It is a source of magnesium and chloride ions.
Products
- Magnesium Phosphate (Mg3(PO4)2): A white, crystalline solid that is insoluble in water. It is the precipitate formed in the reaction.
- Potassium Chloride (KCl): A white, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water. It is the other product formed in the reaction.
Reaction Mechanism
The precipitation reaction between K 3PO 4and MgCl 2proceeds through a series of steps involving the formation and growth of the precipitate.
Formation of the Precipitate
Initially, the ions of K +, Mg 2+, PO 43-, and Cl –are present in the solution. As the reaction progresses, the PO 43-ions from K 3PO 4and the Mg 2+ions from MgCl 2combine to form insoluble Mg 3(PO 4) 2precipitate.
Release of Ions
The formation of the precipitate results in the release of K +and Cl –ions into the solution. These ions remain in solution, maintaining the electrical neutrality of the system.
Growth of the Precipitate
The initially formed precipitate particles act as nuclei for further precipitation. As more Mg 2+and PO 43-ions are released into the solution, they attach to the surface of the existing precipitate particles, causing them to grow in size.
Stoichiometry and Equilibrium
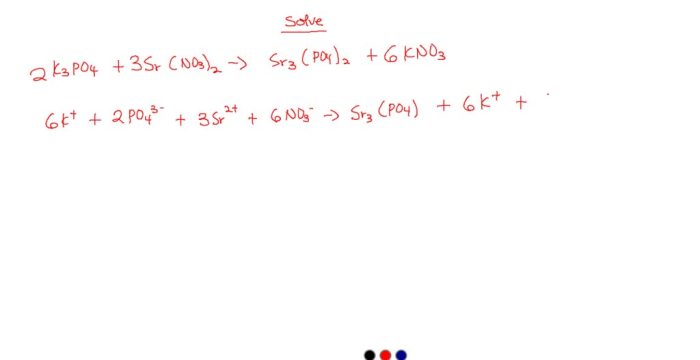
The stoichiometric ratio of the reactants is determined by the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. For the reaction between K 3PO 4and MgCl 2, the balanced equation is:
K3PO 4(aq) + 3MgCl 2(aq) → Mg 3(PO 4) 2(s) + 6KCl(aq)
This equation shows that 2 moles of K 3PO 4react with 3 moles of MgCl 2to produce 1 mole of Mg 3(PO 4) 2and 6 moles of KCl.The equilibrium constant for the reaction is a measure of the extent to which the reaction proceeds.
It is defined as the ratio of the concentrations of the products to the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium. For the reaction between K 3PO 4and MgCl 2, the equilibrium constant expression is:K eq= [Mg 3(PO 4) 2][KCl] 6/ [K 3PO 4] 2[MgCl 2] 3The value of the equilibrium constant can be used to predict the direction of the reaction and the extent to which it will proceed.
A large equilibrium constant indicates that the reaction will proceed to completion, while a small equilibrium constant indicates that the reaction will not proceed to completion.
Experimental Procedures: K3po4 + Mgcl2 Precipitation Reaction

To demonstrate the precipitation reaction between K 3PO 4and MgCl 2, an experiment can be designed using the following steps:
Materials
- Potassium phosphate (K 3PO 4) solution
- Magnesium chloride (MgCl 2) solution
- Two beakers or test tubes
- Stirring rod
- Pipettes or graduated cylinders
Procedure
- Add equal volumes of K3PO 4and MgCl 2solutions to separate beakers or test tubes.
- Stir the solutions thoroughly using a stirring rod.
- Observe the formation of a white precipitate, which is magnesium phosphate (Mg 3(PO 4) 2).
Applications
The precipitation reaction between K3PO4 and MgCl2 has potential applications in various fields, particularly in analytical chemistry and water treatment.
Analytical Chemistry
The reaction can be utilized for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of potassium and magnesium ions in solutions. The formation of a white precipitate of Mg3(PO4)2 indicates the presence of these ions.
Water Treatment
The reaction finds use in water softening, where it helps remove magnesium ions from hard water. The precipitate formed during the reaction settles out, reducing the hardness of the water.
Safety Considerations
The reaction between K 3PO 4and MgCl 2involves the handling of potentially hazardous chemicals, requiring proper safety precautions to minimize risks.
The reactants, potassium phosphate and magnesium chloride, are generally non-toxic and pose minimal health hazards. However, it is essential to follow laboratory safety guidelines when working with any chemicals to prevent accidents or exposure to harmful substances.
Personal Protective Equipment, K3po4 + mgcl2 precipitation reaction
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles to prevent skin and eye contact with the chemicals.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhalation of any fumes or vapors that may be produced during the reaction.
Handling Precautions
- Handle the reactants with care, avoiding spills or contact with skin or clothing.
- If any spills occur, clean them up immediately using appropriate absorbent materials and dispose of them properly.
- Do not ingest or inhale the reactants or products of the reaction.
Waste Disposal
- Dispose of the reaction products and any unused reactants according to established laboratory waste disposal procedures.
- Neutralize any acidic or basic solutions before disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
General Inquiries
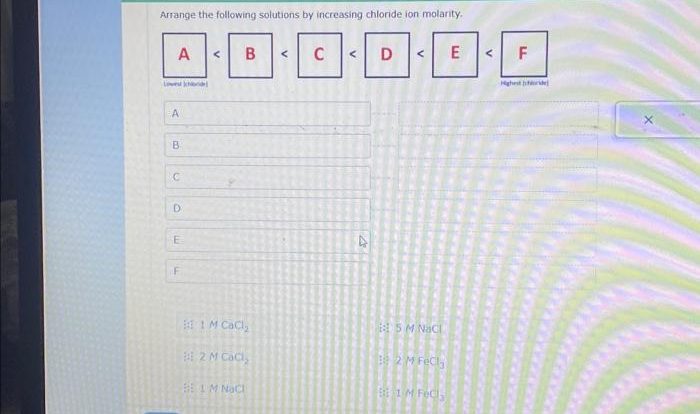
What is the stoichiometric ratio of K3PO4 to MgCl2 in the precipitation reaction?
The stoichiometric ratio is 2:3, meaning that for every 2 moles of K3PO4, 3 moles of MgCl2 are required for complete precipitation.
What is the significance of the equilibrium constant in the K3PO4 + MgCl2 precipitation reaction?
The equilibrium constant provides insights into the extent of the reaction and the solubility of the precipitate. A higher equilibrium constant indicates a more favorable reaction and lower solubility of the precipitate.
What safety precautions should be taken when handling K3PO4 and MgCl2?
Both K3PO4 and MgCl2 are irritants. Proper personal protective equipment (gloves, goggles, lab coat) should be worn, and adequate ventilation should be ensured.