Introducing the Topographic Map Worksheet Answer Key, your ultimate companion for unlocking the secrets of topographic maps. Delve into the fascinating world of map symbols, contour lines, and elevation data, and emerge as a master of terrain interpretation.
Through this comprehensive guide, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and skills to decipher the intricate language of topographic maps, enabling you to navigate landscapes with confidence and make informed decisions.
Topographic Map Basics: Topographic Map Worksheet Answer Key
A topographic map is a detailed and accurate representation of the Earth’s surface, depicting both natural and man-made features. It uses contour lines to represent elevation, providing a three-dimensional view of the terrain.
Topographic maps serve various purposes, including:
- Navigation and orienteering
- Planning and development
- Natural resource management
- Military operations
- Scientific research
Types of Topographic Maps
Topographic maps can be classified based on their scale, content, and purpose:
Scale
The scale of a topographic map refers to the ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. Larger-scale maps provide more detailed information, while smaller-scale maps cover larger areas with less detail.
Content
Topographic maps can vary in the types of features they depict, such as:
- Elevation (contour lines)
- Hydrology (rivers, lakes, streams)
- Vegetation (forests, grasslands)
- Infrastructure (roads, bridges, buildings)
- Cultural features (historical sites, landmarks)
Purpose
Topographic maps can be designed for specific purposes, such as:
- General reference maps
- Specialized maps for hiking, biking, or other outdoor activities
- Maps for military operations
- Maps for engineering and construction projects
Map Symbols and Features
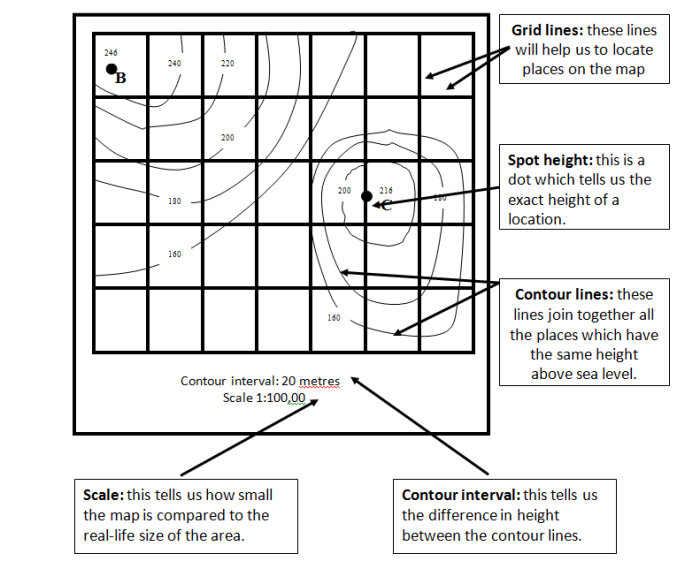
Topographic maps use a variety of symbols and features to represent the physical characteristics of the land. These symbols provide a wealth of information, including the elevation, slope, and landforms of an area.
Understanding these symbols is essential for interpreting topographic maps. Here are some of the most common symbols and their meanings:
Contour Lines
Contour lines are one of the most important features on a topographic map. They connect points of equal elevation, forming lines that show the shape and slope of the land. The closer the contour lines are together, the steeper the slope.
Elevation Data
Elevation data is another important feature on a topographic map. It provides the height of the land above sea level. Elevation data is typically shown in feet or meters.
Other Important Map Features
In addition to contour lines and elevation data, topographic maps also include other important features, such as:
- Rivers and streams
- Lakes and ponds
- Roads and trails
- Buildings and other man-made features
These features help to provide a complete picture of the landscape and can be used to plan routes, navigate, and understand the terrain.
Map Reading and Analysis
Topographic maps provide a wealth of information for understanding the physical features of an area. By analyzing the contour lines, map symbols, and other features, you can gain insights into the terrain, elevation, and other important geographic characteristics.
Determining Slope Using Contour Lines
Contour lines on a topographic map connect points of equal elevation. The spacing between contour lines indicates the steepness of a slope. Closely spaced contour lines represent steep slopes, while widely spaced contour lines indicate gentle slopes.
To determine the slope of a hill, locate two contour lines that represent the top and bottom of the hill. Count the number of contour lines between the two points and measure the vertical distance between them. Divide the vertical distance by the horizontal distance between the two points to calculate the slope in degrees or as a percentage.
Measuring Distances and Areas
Topographic maps have a scale that allows you to measure distances and areas. The scale is usually expressed as a ratio, such as 1:24,000. This means that one unit on the map represents 24,000 units on the ground.
To measure distances, use a ruler or measuring tape to measure the distance between two points on the map. Then, multiply the measured distance by the scale to get the actual distance on the ground.
To measure areas, use a grid overlay or a planimeter. A grid overlay is a transparent sheet with a grid printed on it. Place the grid overlay over the map and count the number of grid squares that cover the area you want to measure.
Multiply the number of grid squares by the area represented by each square to get the total area.
Using Topographic Maps for Route Planning and Navigation, Topographic map worksheet answer key
Topographic maps are invaluable tools for route planning and navigation. They provide information about the terrain, elevation, water sources, and other features that can help you plan a safe and efficient route.
When planning a route, consider the following factors:
- The distance and elevation gain of the route
- The terrain and any obstacles that may be encountered
- The availability of water sources and shelter
- The weather conditions and potential hazards
Once you have planned your route, use the topographic map to guide your navigation. Pay attention to the contour lines to avoid steep slopes or hazardous terrain. Use the map symbols to identify water sources, shelters, and other features that can help you stay on track and safe.
Topographic Map Worksheet Answer Key
This answer key provides detailed explanations and resources for a topographic map worksheet. It covers essential concepts and skills related to map interpretation and analysis.
Questions and Answers
- Question:Identify the contour interval of the map. Answer:The contour interval is 10 feet. This means that each contour line represents a change in elevation of 10 feet.
- Question:Determine the elevation of point A. Answer:Point A is located on the 100-foot contour line. Therefore, its elevation is 100 feet.
- Question:Calculate the slope of the hill between points B and C. Answer:The slope is calculated as the change in elevation (100 feet) divided by the horizontal distance (500 feet). Therefore, the slope is 100 feet / 500 feet = 0.2 or 20%.
- Question:Describe the landform represented by the closed contour lines in the northwest corner of the map. Answer:The closed contour lines in the northwest corner represent a hill. The hilltop is located at the highest point within the closed contours, and the slopes descend away from the hilltop.
- Question:Identify the type of water feature represented by the blue lines on the map. Answer:The blue lines represent streams or rivers. The direction of flow is indicated by the direction of the arrows along the lines.
Additional Resources
Topographic Map Exercises
Topographic map exercises provide users with hands-on practice in reading and interpreting topographic maps. These exercises can range from simple tasks, such as identifying basic map features, to more complex tasks, such as analyzing terrain and determining the best route for travel.
By completing these exercises, users can develop their map-reading skills and gain a better understanding of how to use topographic maps in the field.
Interactive Exercises
Interactive exercises are a great way for users to practice their map-reading skills. These exercises can be found online or in software programs, and they allow users to interact with a topographic map and complete tasks such as identifying map features, measuring distances, and determining elevations.
Interactive exercises can be a helpful way for users to learn about topographic maps and to improve their map-reading skills.
Varying Levels of Difficulty
Topographic map exercises should be designed with varying levels of difficulty. This will allow users to progress at their own pace and to challenge themselves as they improve their skills. Simple exercises can focus on basic map features and tasks, while more complex exercises can involve more advanced concepts such as terrain analysis and route planning.
By providing a variety of exercises, users can find exercises that are appropriate for their skill level and that will help them to develop their skills.
Feedback and Guidance
Feedback and guidance are essential for users to improve their map-reading skills. Exercises should provide feedback to users on their performance, and they should also provide guidance on how to improve their skills. This feedback can be in the form of written instructions, video tutorials, or interactive feedback.
By providing feedback and guidance, users can learn from their mistakes and improve their map-reading skills.
Q&A
What is the purpose of a topographic map?
Topographic maps provide a detailed representation of the Earth’s surface, including its elevation, slope, and other physical features, to facilitate navigation, land-use planning, and environmental studies.
How do I determine the slope of a hill using contour lines?
Contour lines represent lines of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines are spaced together, the steeper the slope.
What are some common topographic map symbols?
Topographic maps use a variety of symbols to represent different features, such as roads, rivers, buildings, and vegetation. A legend on the map will provide the key to understanding these symbols.